Jan 09, 2024 By Triston Martin
Introduction
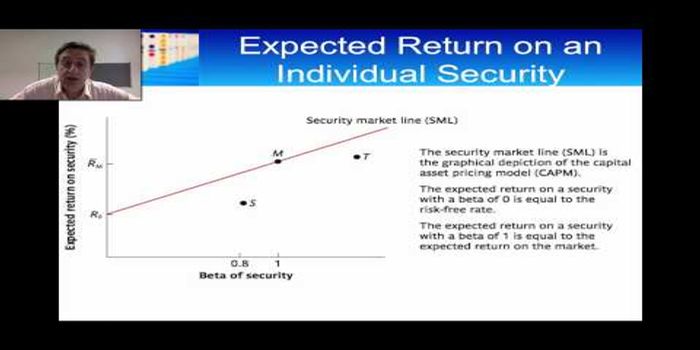
The value of a stock's beta indicates the degree to which its price reacts to movements in the overall stock market. The degree to which a stock is susceptible to the dangers of the market may sometimes be gleaned from comparing its performance to that of a standard index such as the NSE Nifty. With the help of this information, investors can decide whether or not they are willing to take on the additional risk associated with purchasing a stock that strongly correlates to the market.
Examples of Beta
A company's volatility exceeds the market's if its beta value exceeds 1. A high-risk technology corporation returned 175% of the market return over a specific period, according to a beta of 1.75. A stock with a low beta (less than 1) will be less volatile than the market as a whole. An electric utility would have only received 45% of the market's return during the same period, with a beta of 0.45. A company with a negative beta is inversely related to market returns. You would have suffered a two percent loss if the market had increased by 10% and you had invested in a gold business with a beta of -0.2.

How Does It Work?
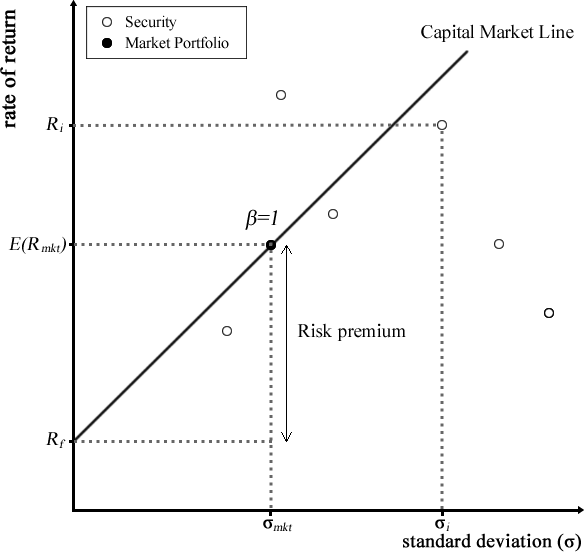
A stock's beta measures its volatility about the volatility of the market. The market defines all other betas, representing a beta of 1. Stocks with a value greater than 1 are thought to be more volatile than the market and, as a result, tend to rise and fall more quickly than the market as a whole. Generally speaking, equities with a beta below 1 are less volatile than the market, but they still rise and fall with the market.
Negative beta securities are relatively uncommon, and their prices typically move against the market. As a result, these securities lose value when the market increases and vice versa. By dividing Apple's covariance with the market, as determined by the Standard & Poor's 500 Index, by the variance of the market's returns about its average return, investors can calculate Apple's beta. The relationship between their movements is quantified by determining the covariance between two securities.
Calculating Beta
Analyzing data using regression is used to calculate beta. It measures how closely a security's returns reflect changes in the market. The covariance of an asset's return with the benchmark's return over a certain period divided by the benchmark's return variance over the same period is known as beta.
- Correlation Variance = Beta
Evaluating a Stock's Beta as an Investor
Investors can use beta in a variety of ways, including:
- To help determine whether a stock is worthwhile purchasing.
- To determine stock price objectives (whether to purchase or sell).
- So that you can determine whether a stock is outperforming or underperforming its risk to determine how adding a stock to a portfolio may affect its volatility.
- To take advantage of a business opportunity or to fortify portfolio defenses.
The Advantages of Beta
Beta is valuable to CAPM supporters. A stock's price volatility is a vital sign of its risk. If the risk is defined as the likelihood of an asset losing value, then beta may serve as a substitute for risk. Intuitively, it makes a tonne of sense. It resembles the price of a stock in a developing technology industry, which is more prone to swings than the market. It's difficult to believe that this stock has lower volatility than a low-beta utility firm.
Issues
When using the beta, you should be aware of the following:
- The estimated beta will be biassed if the securities don't trade regularly.
- The beta may not be a complete indicator of risk.
- Betas may alter over time.
- Betas may vary based on the market's direction (i.e., betas may be greater for down moves than up moves in the market).
The beta measures correlation, not volatility, so keep that in mind. Despite having a beta of zero, a security may be more volatile than the market.
Conclusion
A technique for forecasting an asset's movement concerning the market is called "beta." Stock is more volatile than the market if its beta value is higher than 1, whereas a beta value below 1 denotes lesser volatility. Based on investors' level of risk tolerance, the Capital Asset Pricing Model employs beta to predict the cost of equity financing and the rate of return they might expect. When choosing stocks, the beta has been criticized for its limited utility and lack of understanding of a company's fundamentals. Beta is probably more useful for determining short-term risk than long-term risk.
-

How to Build Credit with Secured Credit Card Rapidly
Feb 04, 2024
-

Men’s Wearhouse Perfect Fit Credit Card
Oct 13, 2023
-

Credit Cards That Offer In-Flight Savings and Bonuses
Oct 15, 2023
-

Everything you Need to Know about Best Credit Cards for Authorized Users
Oct 15, 2023
-

All About Pricing Your Rental Property
Oct 04, 2023
-

Demystifying Payroll Tax Rates: Your Guide to Financial Understanding
Oct 15, 2023
-

Prequalify for Credit Cards: Find the Best Offers from Chase, Discover, Capital One, and More
Oct 09, 2023
-

Follow the leading ones in the mainstream stocks
Jan 05, 2024